HandyTD - Manual Thermal Desorption for Gas Chromatography

HandyTD is a convenient tool that aids the analysis of volatiles and semi-volatiles for the GC and GCMS.
HandyTD Features

Pre-Concentration
- Enhance your GC and GCMS qualitative applications
- Detect even the low concentration compounds in large volume sample
- Use different packing materials to help trap chemicals with different polarity range – ideal for R&D and academic labs

Simple Setup
- The instrument has its own gas control – simply branch out your existing carrier gas flow line
- The size of the tubes used in the HandyTD are ¼” x 3½” ; this is the dimension of the commercially available standard thermal desorption tubes
- Light and portable
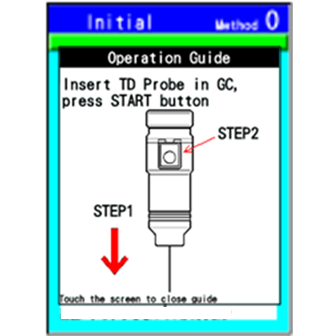
Ease of Use
- HandyTD has a needle that is inserted into the injection port – any sample inlet of any GC or GCMS
- The colour display will guide the user through the operating steps
- Patented technology achieves a fast-heating rate
HandyTD Operation

Figure 1: Target compounds are pre-concentrated in the tube (remove double space), ready for thermal desorption

Figure 2: Target compounds are pre-concentrated in a MonoTrap, ready for direct thermal desorption
HandyTD supports two ways of sample injection. First as shown in Figure 1, target compounds are pre-concentrated in the TD tube before thermal desorption. Second way is as shown in Figure 2, target compounds are pre-concentrated in a MonoTrap (monolithic sorptive material), before direct thermal desorption.
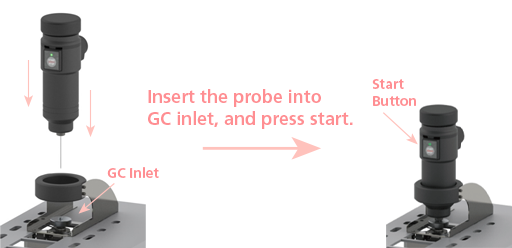
Figure 3: Setting up sample injection using HandyTD
Injection process is straightforward, as shown in Figure 3. HandyTD has a needle that is inserted into the injector port of the GC or GCMS. The internal flow controller of the HandyTD will push the sample to the sample inlet for analysis.
HandyTD Applications
- Concentration analysis of Mikan juice – Using HandyTD Portable Thermal Desorber and MonoTrap Simplified Enrichment Tools
- Concentration analysis of volatile constituents of mosquito incense coil – Using HandyTD Portable Thermal Desorber and MonoTrap Simple Enrichment Tools
- Enrichment Analysis of Volatile Components from Hairbrush ― Sampling Comparisons Between MonoTrap and Sampling Tube
- GC/O Analyses by Simplified Enrichment of Volatile Components in Children's Cold Syrups
Other Sample Introduction Systems

Liquid Injection
In liquid injection, liquid samples are pipetted directly into GC injection port using a needle. This method is used for volatile and semi-volatile analytes. The injection port is preheated to the initial column temperature, allowing evaporation of the solvent and dissolved analytes. However, this high temperature can cause deterioration of peaks on the GC. To avoid this problem, the analytes are usually derivatized in order to block hydrophilic functional groups, lowering their boiling point. The sample can therefore be injected with the port at a lower temperature.

Static Headspace
The static headspace method is used for detection of volatile analytes. In this method, liquid samples are pre-heated in an incubating chamber within the autosampler. This pre-heating causes dissolved components to move freely in equilibrium between the gas headspace and the liquid phase. A higher temperature in the incubation chamber shifts the equilibrium, causing more volatile components to converge in the gas phase. The temperature applied depends on the target analyte. Headspace gas is then sampled and injected directly into the GC.
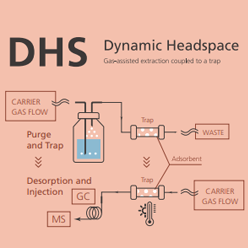
Dynamic Headspace
The dynamic headspace method, also known as “purge and-trap”, is a more sophisticated form of headspace injection which can achieve greater accuracy than SHS. Firstly, a large known volume of inert gas is introduced into the liquid sample, “purging” the sample. The volatile target analytes are swept into an absorbent trap connected to the sample vial. Then the absorbent trap is heated, releasing the volatile analytes into the GC-MS system.
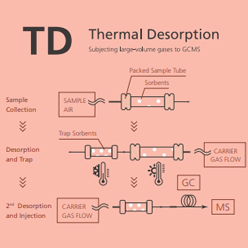
Thermal Desorption
In this method, a portable sampling pump is used for field collection of large volumes of gas in thermal desorption (TD) tubes filled with trap sorbents. Volatile analytes are released from these tubes into the GC-MS via heat desorption using an adsorbent trap system. A good trap system has to be able to accommodate a variety of TD tube types while also allowing optimized desorption conditions for each analyte to ensure precise chromatographic data.
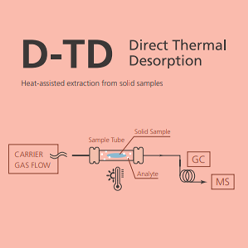
Direct - Thermal Desorption
Direct thermal desorption is used for solid samples rather than gaseous samples as in normal TD. The TD tubes are filled directly with the solid material rather than sorbents. Heating the tubes releases volatile analytes via thermal desorption. These analytes may be introduced directly into the GC-MS or pass through a trap sorbent as in the TD system above.
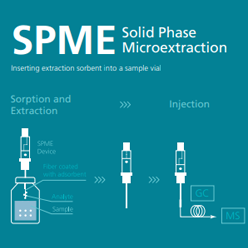
Solid Phase Microextraction
The SPME method is similar to DHS but provides greater flexibility. This method is used for semi-volatile and volatile analytes in liquid or gaseous samples. The SPME sampling needle consists of a fiber core coated with a polymeric stationary phase. It can be inserted directly into liquid samples or into a sample headspace for adsorption of analytes. The needle is then inserted into the pre-heated injection port and releases these analytes into the GC-MS system through heat desorption.
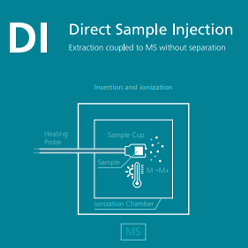
Direct Sample Injection
Direct sample injection is used for small solid or liquid samples that can fit into a small sample cup. The cup is attached to a heating probe and can be inserted directly into the GC-MS ionisation chamber without passing through a GC column. The sample is ionized through heating. This is a useful option for less volatile or non-volatile analytes that are not suitable for GC separation.
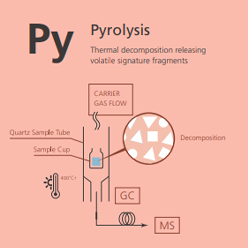
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a unique approach to the analysis of less volatile or non-volatile compounds in liquid or solid samples. The sample is rapidly heated to 600-1000 ºC, releasing smaller, more volatile decomposition products that can be separated and analyzed by GC-MS. The chromatograms/pyrograms obtained in this way can be used as chemical “fingerprints” . Individual mass spectra are used for quality control and component identification.